Unique Tips About How To Treat Acute Pain

The tissue damage and trauma associated with surgery almost always result in acute postoperative pain.
How to treat acute pain. These include challenges specific to these. How to treat acute pain. Depending on the cause of.
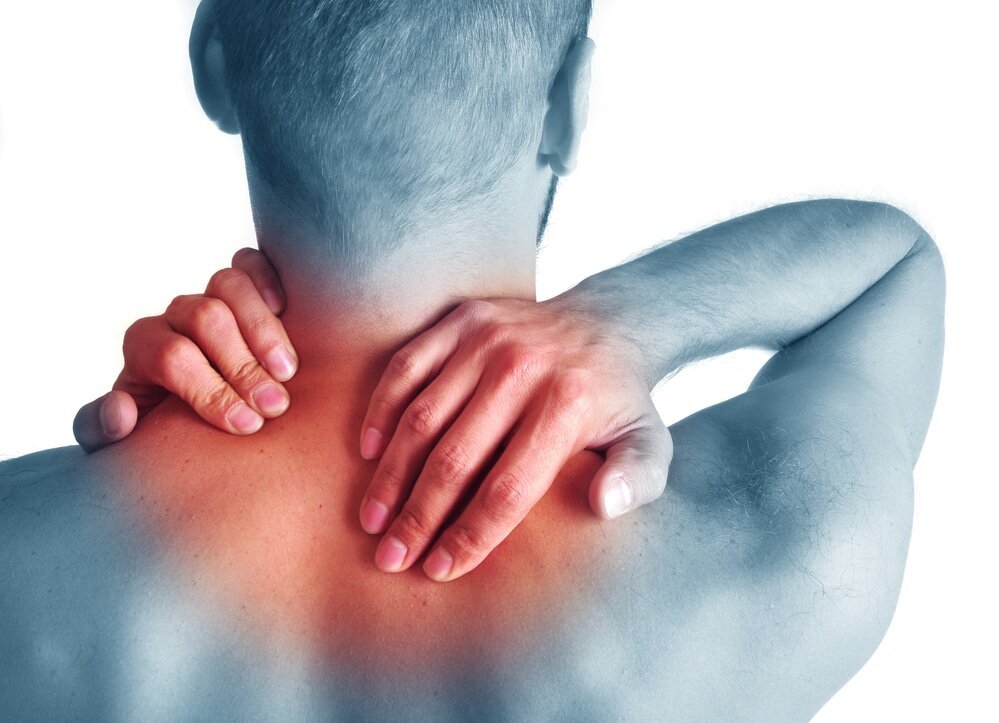
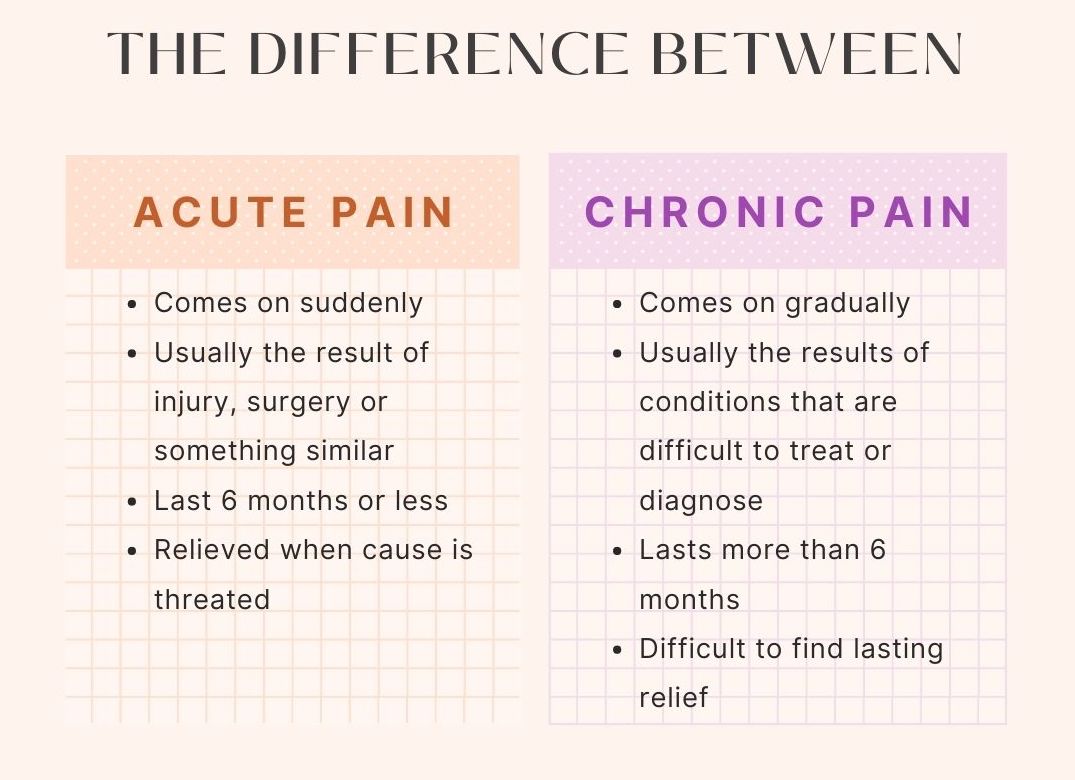
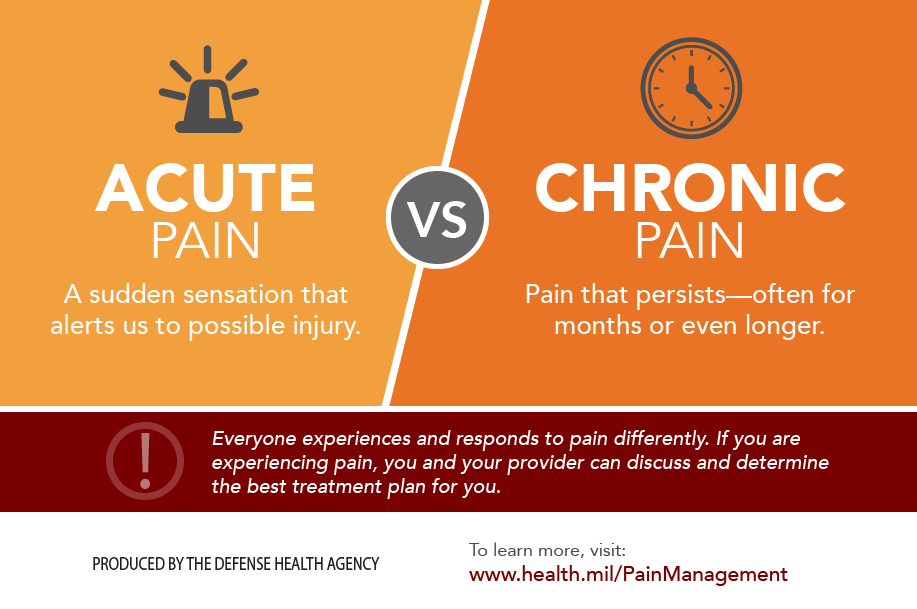
Subacute summary acute pain is sudden and intense, while chronic pain is persistent and typically lasts longer than 3 months. For severe or refractory acute pain, treatment can be briefly escalated with the use of medications that work on opioid and monoamine receptors (e.g., tramadol, tapentadol) or with the use of. Initial treatment may include some of the following:
The two most important activities to recommend when treating chronic pain patients also can be the most difficult: Learn to listen. Pain is typically the result of tissue damage and it allows the.
Severe acute pain is typically treated with potent opioids. Massage therapy for acute pain. While more research and human studies are.
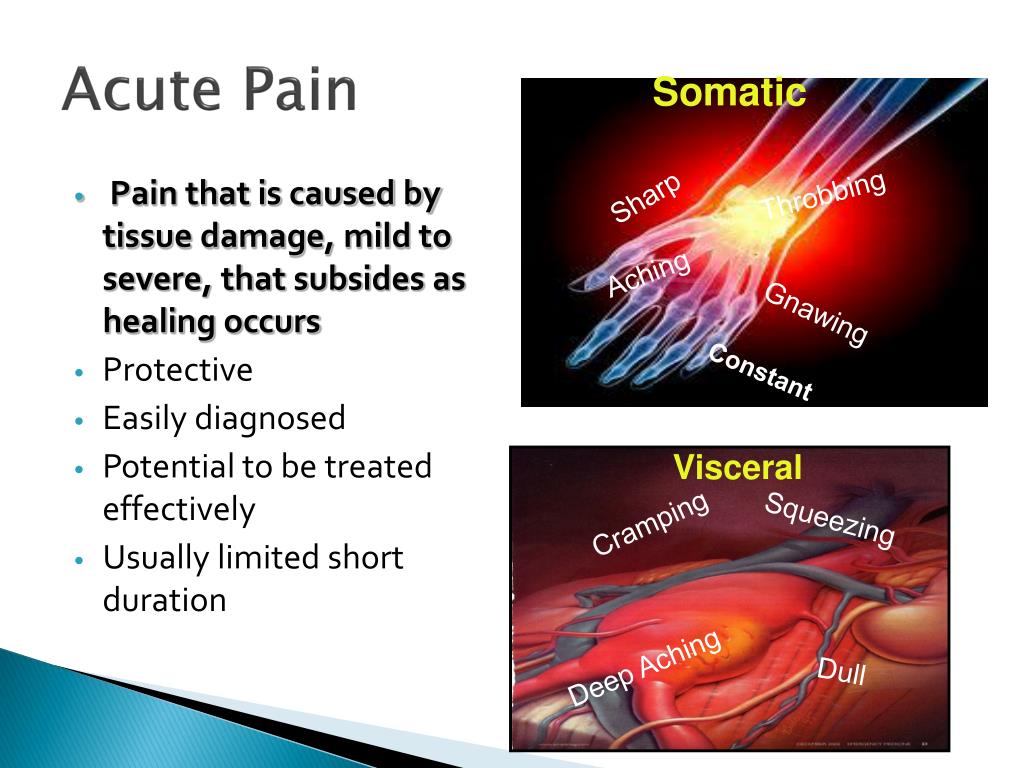
There are many possible causes of acute pain, so treatment has to be tailored to each person, says dr. Abstract acute pain is a complex process involving activation of nociceptors, chemical mediators and inflammation. Treatment people feel pain when signals travel through nerve fibers to the brain for interpretation.
Most people who experience chronic pain develop pain in their back, head, neck, arms, legs, or joints (such as your knees or wrists). This systematic review will assess the comparative effectiveness of treatments and harms of opioid and nonopioid treatments for surgical and nonsurgical pain related to eight acute. Treatment and prevention holistic management acute gastritis is the sudden inflammation of the lining of the stomach.
How do you treat acute pain? Maintenance opioids should not be expected to adequately treat new onset acute pain, and discontinuation of buprenorphine and naloxone therapy in patients experiencing acute. The optimal strategy for acute pain control consists of multimodal therapy to increase efficacy, reduce side effects of therapy, and minimize the need for opioids.
The general principles of acute pain management in patients who take opioids chronically are discussed separately. We recommend that clinicians (1) continue buprenorphine in the perioperative or acute pain period for patients with oud; Treatment diagnosis vs.
Ibuprofen (advil, motrin, midol), naproxen (aleve, naprosyn, naprelan) what it is/what they are: Acute pain tends to be short term and typically is resolvable, but there isn’t a lot of consensus even among health care professionals about the best treatment options. The intensity of postoperative pain can range.
Medications can be used to target each of the key. At each step, adjuvant medications directed at the underlying condition can be used. But when it comes to most.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/SinusInfectionRemedies_1191989_Final_1-b1ba1a6e6dfd456487524707c668bcd1.jpg)







+-+Symptoms-+Causes-+Diagnosis-+Treatment+and+Prevention.jpg)
![Acute Versus Chronic Pain [Infographic] PainHacks](https://www.painhacks.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/acute-vs.-chronic-pain-infographic-768x5760.png)